

5 minute read
Everything (and then some) about blood types
Published July 13, 2023. Last updated January 6, 2026.
Your blood—made of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets¹—is a vitally important fluid. It flows continuously through your blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients throughout your body. But that's not all. It also forms life-saving blood clots, fights infections, removes waste products, and helps keep your body at the perfect temperature. You might not realize it, but your blood is truly one-of-a-kind. Discover what sets yours apart from others.
What exactly is a blood type?
Your blood type is determined by whether (or not) your red blood cells have certain proteins or sugars attached to their surface. These sugars or proteins are called antigens (or blood group markers). Your body uses these antigens to identify which blood cells belong to you, and your immune system recognizes them as your own.
Imagine for a moment that your red blood cells are houses. The antigens on the surface of your red blood cells are like the address on your house. Your immune system is like a mail carrier. The mail carrier will only deliver mail to houses with the right address. If the mail carrier sees a house with a different address, they will not deliver the mail.
In the same way, your body's immune system only recognizes red blood cells with the right antigens. If you receive blood from someone with a different blood type, your immune system will attack the unfamiliar red blood cells—because they have the wrong address. And this is why knowing your blood type is so important.
What are the different blood types?
There are 4 major blood groups:
- A
- B
- AB
- O
What this means is that blood type A only has the A antigen. Blood type B only has the B antigen. Blood type AB has both antigens, but blood type O doesn’t have either of them. There’s also another important protein called the Rh factor (or Rhesus factor). If a person has this protein, they are Rh-positive. If they don’t, they are Rh-negative.
There are many variations of blood types, but these are the 8 most common:
- A+
- A-
- B+
- B-
- AB+
- AB-
- O+
- O-
The plus or minus sign indicates if a person has the Rh factor.
Did you know?
You inherit your blood type from your parents. But even if they have the same blood type - yours could be different.
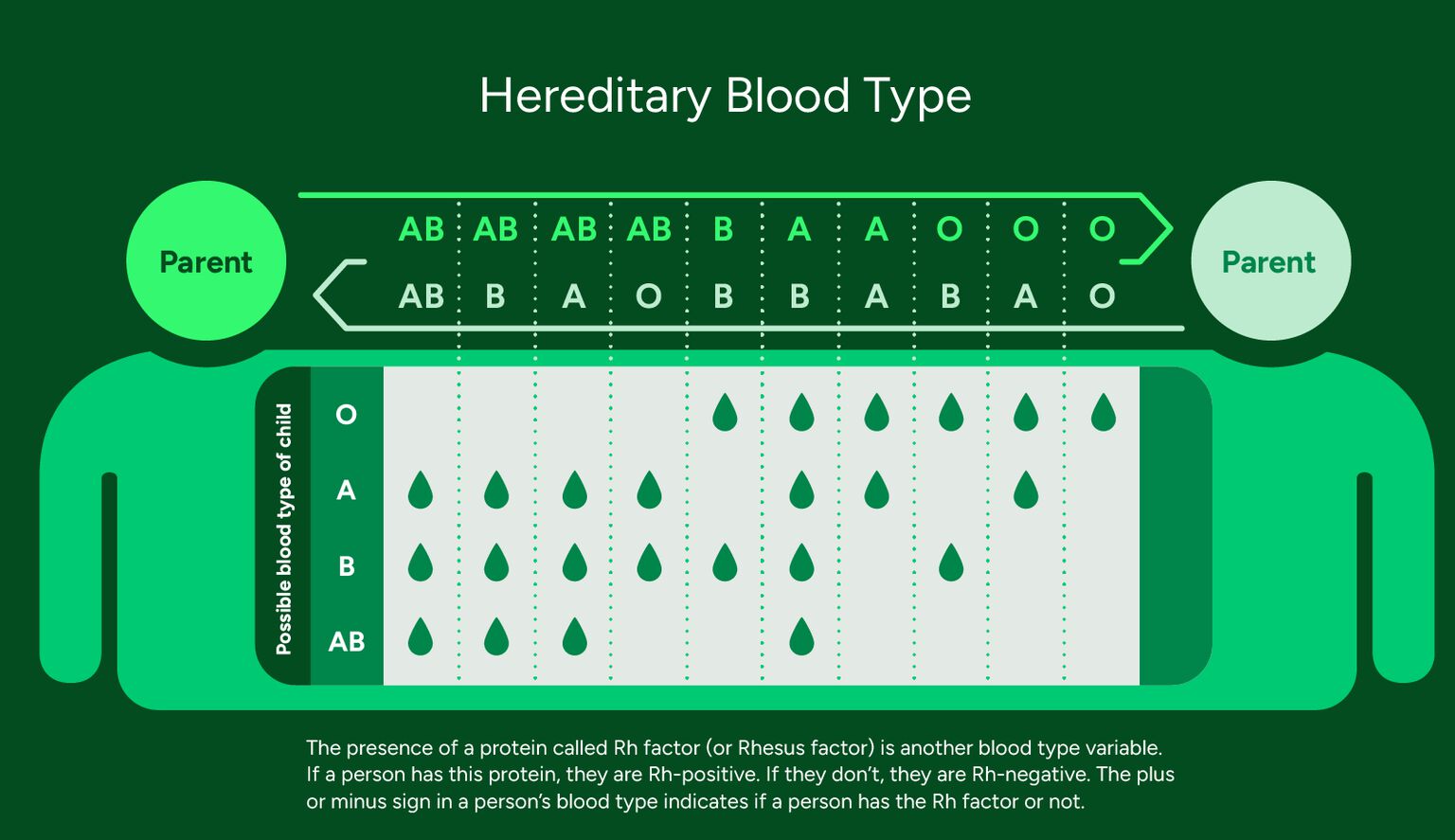

What does it mean to be Rh positive or Rh negative?
Having the Rh factor (or not) doesn’t affect your health.² But it can be important if you’re pregnant. If you’re pregnant and Rh negative, you may need an injection of a blood product called “Rh immune globulin” during your pregnancy. Without this treatment, there’s a risk of Rh incompatibility. Rh incompatibility is when your blood (Rh-) is different from your baby’s blood (Rh+). Because of this difference, your body reacts by producing antibodies (proteins that your immune system makes to fight infection). These antibodies can attack your baby's red blood cells, which can be life-threatening for the baby.
Why is it beneficial to know my blood type?
Knowing your blood type may be more important than you think. One of the most important reasons why you should know your blood type is in case of an emergency. 4.5 million Americans receive a transfusion each year.³ If you ever need a blood transfusion, you will need blood that is compatible with yours. Other important reasons are for:
Donating blood: Donating blood is a selfless act that can make a huge impact on the lives of those who receive it. In fact, type O negative blood is the "universal donor" blood type, which means it can be given to people of any blood type. Only 7% of the population are O negative. So, if you're type O negative, your blood is especially in demand because it’s used most often during emergencies.⁴
But even if you're not type O negative, your blood can still help save lives. Every blood type is needed, and every donation makes a difference.
Planning a healthy pregnancy: Before getting pregnant, there seems to be a lot to consider, including knowing your Rh status. It's an important piece of information that can help prevent potential complications during your pregnancy journey. Remember, your doctor is there for you. They will keep a close eye on you and make sure you get the treatment you may need.
Understanding your health: Your blood type is a part of your unique genetic makeup. It's not just a random assortment of letters and symbols. Your blood type can tell you a lot about your body and your health.
For example, people with type A, B, or AB blood may be at a higher risk for blood clots, while people with type O blood may be more likely to develop stomach ulcers. Certain blood types may also increase your risk of certain health conditions like heart disease and stroke.
Knowing your blood type can help you understand your body better and make informed decisions about your health. It’s also a good idea to talk with your doctor. They can help you understand your risk factors and recommend ways to stay healthy.


What’s the rarest blood type?
AB negative is the least common blood type of the 8 main blood types in the United States. But there are more than 600 blood markers outside the ABO blood system. They have been used to identify over 30 rare blood types. These types of blood can be found in 1 out of every 1,000 people (or fewer). Some of these rare blood groups include the⁴:
- Duffy blood group
- Kell blood group
- Kidd blood group
- Lutheran blood group
But there's one blood type that stands out from the rest—the Rh-null blood type. With fewer than 50 people known to have this blood type, it's truly rare and sometimes referred to as “golden blood.”
What’s the most common blood type?
O positive is the most common blood type in the United States. This type of blood is also the most needed since it’s given to patients more than any other type.
O positive red blood cells aren’t compatible with all blood types. But they are compatible with any positive blood type (A+, B+, AB+, O+). People with O positive blood can only receive blood transfusions from O positive or O negative blood types.
If you have O positive blood, please consider donating. Because of its high demand, O positive blood is one of the first to run out during a shortage. You could help save the life of someone in need.
Can my blood type change?
Usually, your blood type doesn’t change throughout your life. But there are some rare cases where it can happen. Potential causes are bone marrow transplants or certain types of infections or leukemia. It’s important to note that not all these changes in blood type are permanent.
Your blood type is part of your genetic makeup, and it can tell you a lot about your health. Knowing your blood type is important. And one day, it may just save a life—or your own.
Do you know your blood type?
Get results online, fast. Our Blood Type Test identifies your blood group (A, B, AB, or O) and if you’re Rh positive or negative. It’s easy to buy a test on questhealth.com, and simple to schedule an appointment at a nearby Quest Diagnostics location.
No doctor visit is required to buy your own lab test at questhealth.com. PWNHealth and its affiliates review your purchase to ensure it is medically appropriate before submitting the test order for processing. PWNHealth also reviews your test results and will contact you directly if they require prompt attention. Included in each purchase is the ability to discuss your test results with an independent healthcare provider; however, you are also encouraged to speak with your primary healthcare provider.
Tests featured in this article:
References
- American Society of Hematology. Blood basics. Accessed June 19, 2023. https://www.hematology.org/education/patients/blood-basics.
- Cleveland Clinic. Rh Factor. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21053-rh-factor.
- American Red Cross. Know Your Blood Type. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://www.redcrossblood.org/donate-blood/blood-types/know-your-blood-type.
- American Red Cross. Facts About Blood and Blood Types. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://www.redcrossblood.org/donate-blood/blood-types.
- Cleveland Clinic. Blood Types. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21213-blood-types.
Sources
- Medline Plus. Blood Typing. Accessed June 19, 2023. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003345.htm.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The Rh Factor: How It Can Affect Your Pregnancy. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/the-rh-factor-how-it-can-affect-your-pregnancy.
- American Red Cross. Facts and Blood and Blood Type. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://www.redcrossblood.org/donate-blood/blood-types.html.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens. Accessed June 19, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2261.
- Abegaz SB. Human ABO Blood Groups and Their Associations with Different Diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6629060. doi:10.1155/2021/6629060
- Quest Diagnostics. More Americans Know Their Horoscope Sign Than Their Blood Type, Survey Reveals. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://newsroom.questdiagnostics.com/2023-01-23-More-Americans-Know-Their-Horoscope-Sign-Than-Their-Blood-Type,-Survey-Reveals.
- WebMD. How Your Blood Type Can Affect Your Health. Accessed June 22, 2023. https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/ss/slideshow-how-your-blood-type-affects-your-health.
- American Red Cross. Why is Type O Blood So Important? Accessed June 22, 2023. https://www.redcrossblood.org/donate-blood/blood-types/o-blood-type.
Remove Product?
Shop Tests
Top Nav Jump Mobile
Top Nav Jump Shop Tests
Top Nav Jump Help Me Choose
Top Nav Jump Discover
Verify that it's you
We sent a verification code to
Haven't received a code or need a new code? Resend a new code
It may take a minute to receive your code. Be sure to check your email filter or spam folders.
All rights reserved. Copyright 2023
Address Verification
Quest does not currently support P.O. Box addresses, please update to a valid address.


